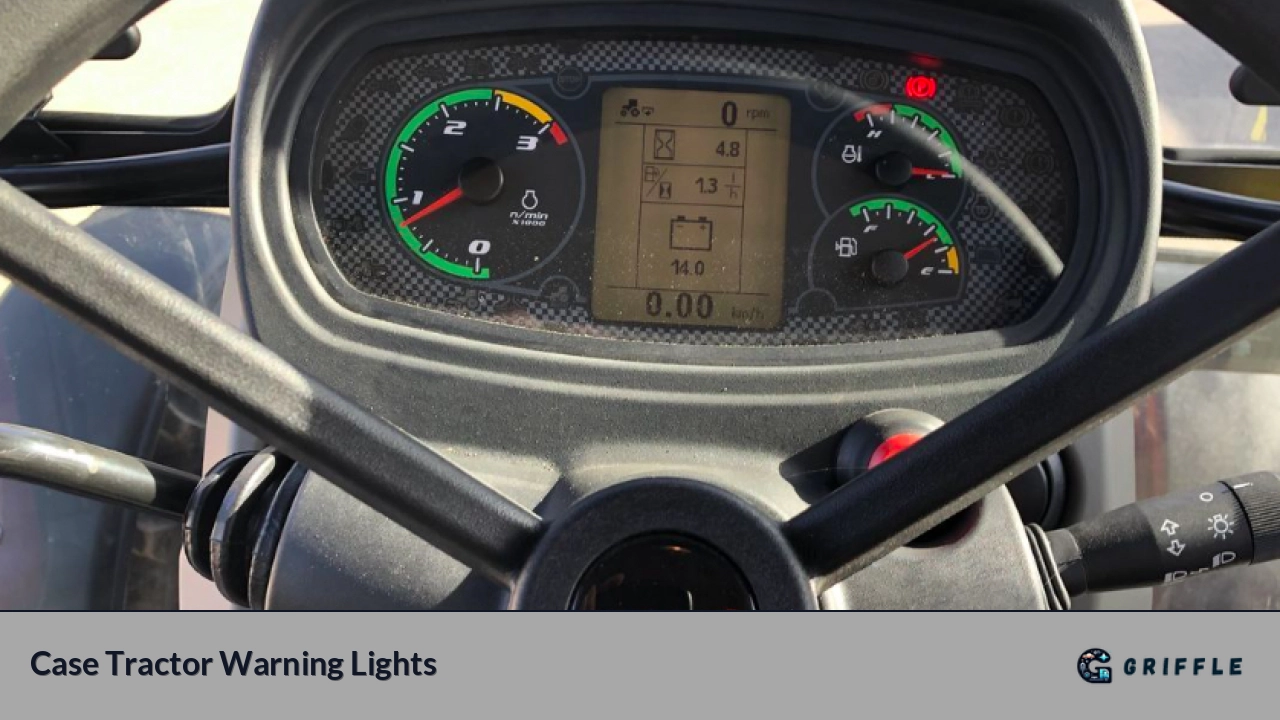
Understanding the significance of warning lights on a Case tractor ensures your safety. This post will guide you through the various warning lights and their meanings, helping you to navigate potential dangers effectively. Let's start by explaining a Case tractor's warning lights and symbols. Then, we'll dive into the implications of each light and why they demand your attention. Lastly, we'll provide essential safety tips for operating a Case tractor.
What Does Case Tractor Warning Lights Mean?

Recognizing the warning lights when operating a Case tractor is essential for avoiding hazards. The tractor has position lights at the front and rear that signal whether it's moving forward or reverse.
Additionally, the activation of the PTO is indicated by a specific warning light, and if equipped, side markers will show the tractor's travel direction. It's important to be familiar with these basic indicators - the position lights and the PTO switch warning light - as they inform you of the tractor's movement and the PTO's status. The side markers also guide the tractor's direction, enhancing your safety while working.
Operating a tractor combines enjoyment with potential risks, particularly if you must know what the warning lights signify. Common alerts may indicate issues like a damaged front loader arm, an imbalanced load, or low fuel. Recognizing these signals can prevent accidents and ensure a safe tractor operation. For instance, lights that warn of a broken arm, an imbalance, or low fuel necessitate immediate action to rectify the issue before continuing to operate the tractor.
Additionally, symbols accompanying the warning lights, such as a 'W' next to a low fuel indicator, prompt specific actions like refueling. Knowledge of these warnings allows for a secure and enjoyable tractor operation experience.
Case Tractor Warning Lights Types
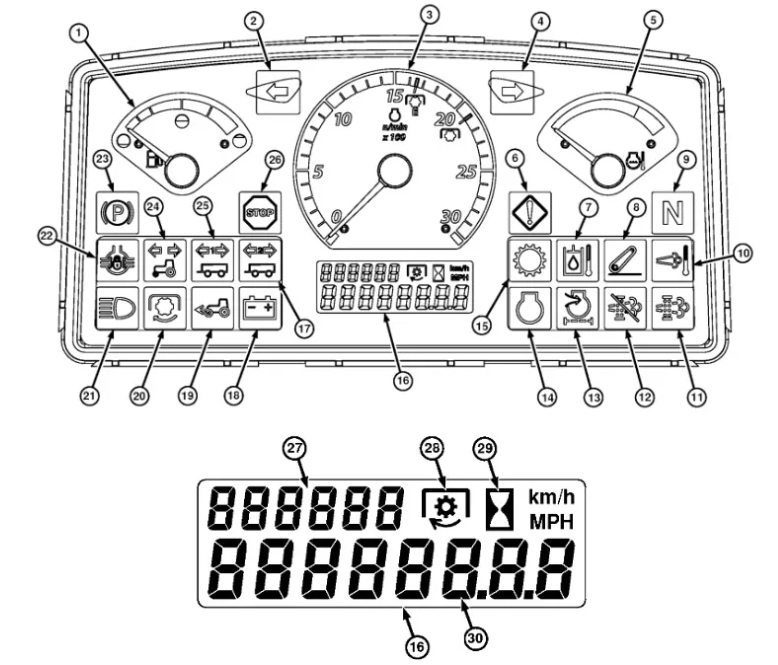
Case tractors utilize warning lights to signal potential hazards, ensuring operator safety. Recognizing the different lights and their meanings is key. The primary warning lights include red and green, indicating problems with the blade or transmission; double yellow, signifying the need for hydraulic system attention; and single orange, alerting to a possible power failure. Familiarizing yourself with these alerts will prepare you for quick action in emergencies.
Case tractor warning lights are crucial for maintaining safety and efficiency during operation. By understanding the significance of these lights, you can preemptively address issues, preventing accidents and saving valuable time. This table will cover the most prevalent warning lights you might encounter:
| No | Indicator Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fuel Level Gauge | Indicates the amount of fuel left in the tank. |
| 2 | Left Turn Indicator | Signals when making a left turn. |
| 3 | Tachometer | Displays the engine's revolutions per minute (RPM). |
| 4 | Right Turn Indicator | Signals when making a right turn. |
| 5 | Engine Coolant Temperature Gauge | Shows the engine coolant temperature. A red zone indicates overheating; turn off the engine to prevent damage. |
| 6 | Service Alert Indicator | Alerts to a system malfunction. |
| 7 | Hydraulic Oil Temperature | Indicates excessive hydraulic oil temperature. |
| 8 | Electrohydraulic Hitch Indicator | Shows a malfunction in the hitch system. |
| 9 | Neutral Indicator | Shows the transmission reverser is in neutral. Flashing indicates improper shifting. |
| 10 | High Exhaust Temperature Indicator | Alerts to high exhaust filter temperatures during cleaning. |
| 11 | Exhaust Filter Indicator | Indicates the exhaust filter is full of soot and requires cleaning. |
| 12 | Exhaust Filter Disabled Indicator | Shows the exhaust filter cleaning function is disabled. |
| 13 | Engine Air Cleaner Restriction Indicator | Indicates the air cleaner element is clogged. |
| 14 | Engine Information Indicator | Alerts to an engine malfunction. |
| 15 | Transmission Information Indicator | Indicates a malfunction in the transmission system. |
| 16 | Information Display | Displays vehicle metrics and diagnostic codes. |
| 17 | Trailer 2 Indicator | Flashes with the trailer's turn signals or hazard lights. |
| 18 | Charging System Indicator | Indicates a malfunction in the alternator. |
| 19 | MFWD Engaged Indicator | Indicates the mechanical front-wheel drive is engaged. |
| 20 | PTO Engaged Indicator | Shows when the rear Power Take-Off (PTO) is activated. |
| 21 | High Beam Indicator | Indicates the headlights are on high beam. |
| 22 | Differential Lock Indicator | Indicates the differential lock is engaged. |
| 23 | Park Brake Indicator | Shows the parking brake is engaged. |
| 24 | Vehicle Indicator | Flashes with the vehicle's turn signals or hazard lights. |
| 25 | Trailer 1 Indicator | Flashes with the trailer's turn signals or hazard lights. |
| 26 | STOP Indicator | Indicates a severe malfunction; shut off the engine immediately and check for issues. |
| 27 | Vehicle Information Display | Displays fault names in diagnostic mode and vehicle metrics like wheel speed and engine hours. |
| 28 | PTO Icon | Indicates the Power Take-Off (PTO) speed setting. |
| 29 | Hour Meter Icon | Displays engine hours. |
| 30 | Vehicle Information Display | Shows wheel speed, engine hours, PTO speed, and diagnostic codes. |
1- Fuel Level Gauge
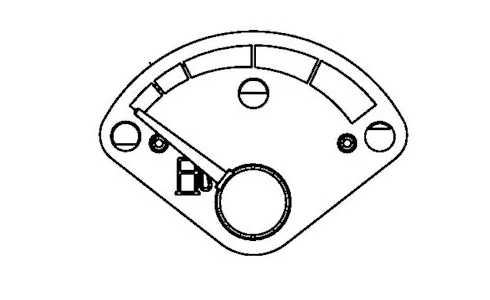
The gauge tracking the tractor's fuel is indispensable for monitoring its remaining amount. It enables operators to manage fuel consumption wisely and schedule refills ahead of time, avoiding the inconvenience of halting operations unexpectedly due to fuel depletion. Keeping a close watch on this gauge allows operators to ensure ample fuel for the job, streamlining work plans and minimizing idle time.
To avoid warnings from the fuel level gauge, consistently check the connections and fuel sensor. If the indicator shows incorrect readings, evaluate the fuel gauge sender for signs of damage or wear and replace it as needed. Cleaning the contacts regularly can also prevent potential problems.
2- Left Turn Indicator
Activating this indicator communicates the tractor's intent to turn left, boosting safety on both roads and fields. It notifies other drivers and operators about the tractor's forthcoming direction, lessening the likelihood of mishaps. This feature is crucial for conveying turning intentions clearly when visibility is poor or operating close to vehicular traffic.
Inspect and replace any non-functioning bulbs to prevent the left turn indicator light from coming on. Examine the turn signal switch and its wiring for any defects and carry out repairs or replacements as needed to ensure the signal remains clear.
3- Tachometer
The tachometer, indicating engine speed in revolutions per minute (RPM), is key to understanding the engine's operational state. By observing the RPM, operators can fine-tune the engine's performance and fuel efficiency, steer clear of excessive revving, and keep the engine operating within safe parameters, prolonging its service life.
It's important to avoid inaccuracies on the tachometer and regularly check the engine. Problems typically stem from the vehicle's electrical system; thus, maintaining secure and clean connections is crucial.
4- Right Turn Indicator
Mirroring the function of the left turn indicator, this light denotes the intent to turn right. It's essential for clear communication with other road users or those in the field, making movements predictable and clear. This, in turn, promotes safety during operations and helps avoid accidents.
Maintenance of the right turn indicator parallels the left, focusing on bulb upkeep and inspecting the switch and wiring for any impairments to ensure reliable signaling.
5- Engine Coolant Temperature Gauge
This gauge shows the temperature of the engine coolant, which is vital in averting overheating and consequent engine damage. The gauge's red zone alerts operators to high temperatures that may signal issues such as a low coolant level, a dirty radiator, or a blocked screen, necessitating immediate action to protect the engine.
Inspect the coolant level, keep the radiator clean, and check the coolant system for any signs of leaks. Additionally, replace the thermostat promptly if it fails to open, which can lead to overheating.
6- Service Alert Indicator
This light signals an issue within the tractor's systems, urging the operator to consult the information display for error messages and seek servicing when needed. Such alerts are crucial for catching and addressing small problems before they escalate, safeguarding the tractor's reliability and extended use.
Ensure your tractor undergoes routine servicing, including checking all fluids and filters and performing maintenance tasks as recommended to maintain optimal performance.
7- Hydraulic Oil Temperature Light
When this indicator lights up, the hydraulic oil temperature is too high, which could decrease oil quality and cause hydraulic system issues. Keeping an eye on this indicator is essential for the system's efficiency and avoiding operational problems.
The hydraulic oil level should be checked and maintained regularly, and the oil or filter should be replaced if overheating occurs. The oil's cooling system must also work properly to prevent overheating alerts.
8- Electrohydraulic Hitch Indicator
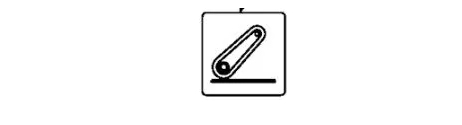
This indicator alerts the operator to issues within the tractor's hitch system, advising the operator to check for error messages. Prompt diagnosis and resolution ensure the hitch system remains in good working condition, which is vital for efficient implementation attachment and task execution.
Conduct regular inspections and maintenance to avoid malfunctions. Make sure tight electrical connections and the hydraulic system are leak-free.
9- Neutral Indicator
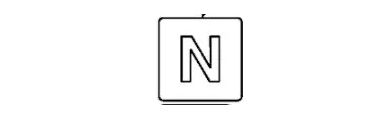
This light confirms the transmission reverser is in neutral and blinks if incorrect shifting occurs, providing essential feedback for safely starting or stopping the tractor.
Maintain regular checks on the transmission fluid, ensuring proper adjustment and lubrication of the mechanism to avoid incorrect neutral indications.
10- High Exhaust Temperature Indicator
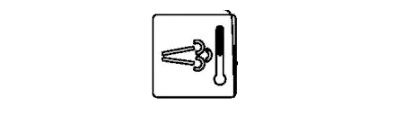
This indicator warns of high exhaust system temperatures, typically during filter cleaning. Recognizing elevated exhaust temperatures is crucial for managing operations during these periods and ensuring the exhaust system's proper function.
Inspect the exhaust system for blockages regularly and ensure the filter cleaning process works as intended. Do not turn off the exhaust filter cleaning feature unless necessary, and investigate any high-temperature readings for potential obstructions in the system.
11- Exhaust Filter Light
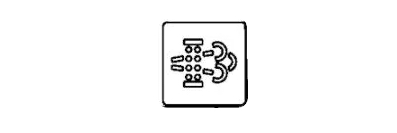
The light indicating the need for exhaust filter maintenance turns on when it detects a high level of soot, signaling the necessity for a cleaning cycle. To keep the tractor running smoothly, avoid blockages, and comply with emission standards, it's vital to clean the exhaust filter regularly. Overlooking this alert may result in decreased efficiency and higher fuel usage.
Ensure you drive the tractor under conditions that support passive regeneration by maintaining a load factor over 30% for effective natural cleaning. In cases where active regeneration is needed, operate the tractor with a sufficient load for about 20 to 30 minutes to increase exhaust heat and trigger the cleaning process.
12- Exhaust Filter Disabled Indicator
This light activates to show that the exhaust filter's cleaning capability has been turned off manually. Although this might be required in some situations, deactivating the cleaning feature can cause soot to build up, possibly degrading the tractor's function and emission controls.
To prevent problems related to the deactivation of the exhaust filter cleaning, avoid turning it off unnecessarily. If you need to turn it off, reactivate the system as soon as possible to keep the exhaust filter working correctly and minimize soot accumulation, which can impair performance and elevate emissions.
13- Engine Air Cleaner Restriction Indicator
This indicator alerts the operator when the air cleaner becomes blocked. Maintaining a clear air intake is essential for the engine's efficiency and durability. Ignoring this warning can cause a drop in engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and risk of engine harm. It's advisable to check regularly and, if necessary, replace the air cleaner element to guarantee the engine operates at its best.
To avoid the air cleaner blockage indicator from coming on, clean or replace the air cleaner element routinely. Keeping the air cleaner in good condition prevents obstructions, ensuring the engine runs efficiently.
14- Engine Information Light
This light warns of issues within the engine system, urging the operator to check oil levels and the information display for error messages. Addressing engine alerts swiftly can prevent small problems from escalating, safeguarding the engine's performance and dependability.
It's important to regularly monitor and maintain the engine's oil properly, including changing the oil and filters as needed. If the engine information system indicates any error messages or faults, act quickly to avoid significant engine damage.
15- Transmission Information Light
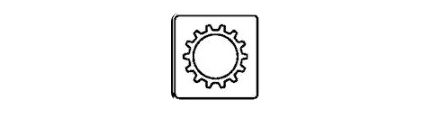
Activating this light signals a problem within the transmission system, prompting the operator to check for error messages and seek professional service. Keeping the transmission in top condition is crucial for the tractor's smooth operation and to avert malfunctions that could interrupt essential tasks.
Ensure the transmission fluid is kept at the recommended level and quality. Conducting regular inspections and changing the fluid as needed helps avoid transmission complications. Should the light turn on, examine the transmission for wear or damage and resolve any issues promptly.
16- Information Display
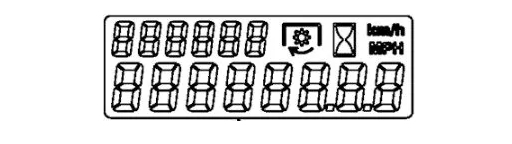
The digital hub displays vital information about the tractor, such as speed, operating hours, gear selection (for models so equipped), PTO speed, and diagnostic codes. This centralized information center aids operators in effectively monitoring the tractor's status and maintenance requirements, enabling well-informed operational and maintenance decisions.
Stay vigilant for any alerts or maintenance signals on the display. Adhering to maintenance schedules and addressing alerts swiftly can forestall significant issues, ensuring efficient tractor operation.
17- Trailer 2 Indicator
This indicator blinks to show the activation of the trailer's turn or hazard lights, aligning the tractor's signals with the trailer for improved safety and communication on roads or within farm operations.
Check that all trailer lighting, including turn and hazard signals, functions properly. Conduct regular inspections and immediately fix any issues with bulbs or wiring to prevent this indicator from activating unnecessarily.
18- Charging System Light
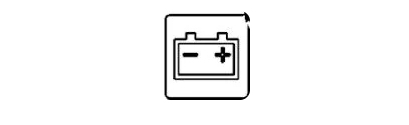
When lit, this light warns of issues with the alternator or the tractor's charging system. This system is critical for maintaining the battery's charge and powering the tractor's electrical components. Address any charging system problems quickly to avoid electrical failures hindering tractor functions.
Frequent checks and maintenance of the electrical system, including the alternator and battery, can help avoid problems with the charging system. If this light comes on, inspect the charging components for any signs of wear or damage and replace them if necessary.
19- MFWD Engaged Indicator
This indicator confirms the mechanical front-wheel drive (MFWD) engagement. This enhances the tractor's grip and stability on challenging terrains and verifies the activation of MFWD, optimizing the tractor's performance for varied tasks.
Activate the MFWD only when needed to reduce wear. Ensure the system is inspected regularly to keep functioning correctly and address any issues quickly to preserve the tractor's traction and efficiency.
20- PTO Engaged Indicator
This light turns on to indicate that the rear Power Take-Off (PTO) is in use, showing that it's currently powering attached tools or machinery. Monitoring the PTO's status is key for safely attaching or removing implements and during upkeep.
Make sure to engage the PTO properly and only as required. Conducting routine checks and maintenance on the PTO system, including assessing wear and ensuring it's well-lubricated, helps avert problems and keeps the PTO engagement indicator accurate.
21- High Beam Indicator
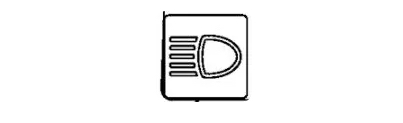
This indicator shows when the tractor's high-beam headlights are used, enhancing visibility for night work or in low-light environments. Operators must judiciously switch between high and low beams to maintain safety for themselves and others.
High beams should be used judiciously, switching to low beams for oncoming traffic to avoid blinding other drivers. Headlight bulbs must be inspected and replaced regularly to maintain the high beam indicator's reliability.
22- Differential Lock Indicator
This light illuminates to show the differential lock is active. This feature, which boosts traction by making both wheels on an axle rotate simultaneously, is useful in slick or uneven conditions. It should be used as needed to increase stability and prevent slipping.
Activate the differential lock only when necessary for better grip and disengage it once conditions improve to reduce drivetrain wear. Keeping the differential lock mechanism well-maintained ensures the indicator works properly.
23- Park Brake Light
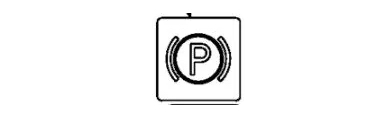
This indicator signals that the parking brake is applied, securing the tractor against unintended movement. It reminds the operator to release the parking brake before driving and to use it when stationary to prevent the tractor from rolling.
Always apply the parking brake securely when the tractor is stationary. Before driving, ensure the parking brake is released to avoid damage to the engine and drivetrain. Routine inspections and adjustments of the parking brake mechanism are crucial.
24- Vehicle Indicator
This light flashes to indicate that the tractor's turn signals or hazard lights are on. These signals indicate turns or warn of danger and are critical in signaling the operator's intentions to others. This is crucial for safety during use in various environments.
Ensure the tractor's signaling lights, including turn and hazard lights, are checked regularly and replace any non-functioning bulbs. Maintaining the lights' wiring and fuses in good condition ensures the indicator functions effectively.
25- Trailer 1 Indicator
Similar to the Trailer 2 signal, this light blinks when the first trailer's turn or hazard lights are used, aligning the tractor and its trailers in signaling to enhance safety and communication during movement or fieldwork.
Maintain the trailer's lights and electrical connections through regular checks to ensure synchronization. Proper upkeep of the trailer's lighting system helps avoid malfunctions with this indicator.
26- STOP Light

This crucial light turns on to alert operators of an immediate system malfunction that demands swift action. The engine should be stopped immediately, and the system's error messages should be reviewed to prevent further damage and ensure operator safety.
Monitor the tractor's systems regularly and address any errors immediately. Adhering to the manufacturer's maintenance schedule can help prevent situations that would activate this warning light.
27- Vehicle Information Display
This screen displays vital information, including gear settings for models equipped with Hi/Lo transmissions. In diagnostic mode, it offers:
- Detailed error analysis
- Pinpoints specific system issues
- Facilitates targeted maintenance
Regularly checking this screen for alerts or maintenance prompts helps prevent significant issues and ensures the tractor runs smoothly.
28- PTO Icon
This symbol shows the PTO speed, signifying the tractor is set to operate implements at this specified speed. Monitoring the PTO's setting is essential for using machinery effectively and ensuring tasks are performed at the appropriate speed for the best results and safety.
Engage the PTO carefully and only when necessary. Maintaining the PTO system, including performing wear checks and lubricating it, ensures its indicator works correctly.
29-Hour Meter Icon
This icon appears when the tractor's total engine operating hours are shown on the Vehicle Information Display. Keeping track of engine hours is crucial for timely maintenance, which helps keep the tractor in peak condition.
Use engine hours as a guide for scheduling regular maintenance. Following a maintenance plan based on engine hours helps avoid potential issues and keeps warning indicators at bay.
30- Vehicle Information Display
This panel shows essential data such as wheel speed, engine operating time, PTO speed, and diagnostic codes, serving as the central point for tracking the tractor's condition and maintenance needs.
Maintain the display's functionality by promptly addressing any indicated problems. Regular software updates, if available, and keeping the display clean enhance its reliability.
Last Words
In conclusion, comprehending the significance of Case tractor warning lights is paramount for ensuring both safety and efficiency in tractor operations. The appearance of a red warning light typically signals a grave concern, such as engine overheating or a low fuel condition, which should not be ignored due to the risk of inflicting severe and expensive harm to the tractor's engine. Immediate attention to any issue flagged by the red light is crucial to avert further damage.
Beyond the red warning light, operators must familiarize themselves with other indicators and symbols that provide quick insights into the tractor's status. Normally, these indicators will show green, signifying that all systems are functioning properly.
Regular maintenance and checks are essential to the tractor's safety and performance. This encompasses monitoring oil and fluid levels, assessing tire condition, and verifying the operational status of all warning lights and symbols. Adhering to these maintenance protocols can help prevent accidents and extend the lifespan of Case tractors.
To summarize, a deep understanding of the meanings behind Case tractor warning lights is vital for safe and effective tractor use. By remaining vigilant about these warnings and adhering to routine maintenance schedules, operators can avoid potential mishaps and ensure their tractors perform optimally.
📌 Suggested article: Kioti Tractor Warning Lights Meanings
🔍 Explore more: Mahindra Tractor Warning Lights And Symbols
🛠️ Handy resources: Tractor Dashboard Symbols and Warning Lights






